If you have a website, you’ve probably heard about the importance of internal linking. But how exactly will internal links help your ecommerce website? And how can you maximize its benefits for your business?
Read on, as you’re about to learn.
What Is Internal Linking: Definition and Importance
Internal linking is connecting one page of your website to another through hyperlinks, on the same domain name. This way, you create an internal network of relevant information that will benefit both your visitors and search engine crawlers. If they can rely on your internal links, your audience (and potential customers) know exactly where they are and where to find the important stuff on your website.
Search engines also love internal links pointing to your web pages. A solid internal linking structure helps search engine crawlers understand which sites and pages in your site are important and how they relate to each other. A solid internal linking strategy for online businesses like yours will boost SEO and website authority.
By properly linking product pages, category pages, and other relevant content, you improve visibility on search engine result pages (SERPs). This is critical, especially for Philippine e-commerce, with its 73 million strong, active online users. You need to put your stuff where your audience can see them.
Understanding Link Juice and PageRank Flow
If you want to maximize your online visibility and authority, you need to know the link juice concept- often referred to as link equity or link value.
Link juice refers to the authority passed from one page to another through hyperlinks. It’s the ranking power that flows to the linked page. This passed power increases how important the linked page is in the eyes of search engines.
PageRank flow is a measurement developed by Google to assess web page importance based on the links pointing to them. If your website has good internal linking, link juice is efficiently shared, and you will tend to have a high PageRank flow score.
Both of these elements directly impact your website’s ranking. Internal linking is critical here. By interconnecting product pages, category pages, and other relevant content, internal linking ensures that link juice flow is optimized.
This strengthens the authority of individual pages and contributes to the overall SEO health of your e-commerce platform.

How to Use Internal Linking on Your E-commerce Website
Now that you’re familiar with the internal linking and its importance for your ecommerce business, it is time to dig deeper into the topic.
In the next section, you will learn how to properly place and use internal links across your website, so you can increase its overall authority and search engine visibility.
Navigation and User Experience: Guiding Users through Your Website
Improving user experience should be one of your main priorities if you want to sell anything online. A seamless and intuitive navigation experience is critical. These factors directly impact all important metrics measured through ecommerce analytics tools, such as bounce rate, conversion rate, and overall customer satisfaction.
Internal linking improves navigation and user experience. Strategic linking creates an interconnected web of content your visitors can easily navigate. This reduces bounce rates and encourages users to explore more, potentially increasing conversions.
You can do that by creating compelling calls-to-action as internal links to guide users towards desired actions or important pages, incorporating internal links within navigation menus to provide users with direct access to key pages, and optimizing footer and sidebar links.
Establishing Website Hierarchy: Organizing Content with Internal Links
When creating an e-commerce website, your customers must immediately grasp how your website works. Having a robust website hierarchy is critical to this.
Here’s how you can implement it:
- Strategically link products: Strategically add internal links to connect related products within category and subcategory pages encourages your customers to explore.
- Utilize breadcrumb navigation: Implement breadcrumb links to show your customers their location within the site hierarchy.
- Incorporate hub pages: Create central hub pages for specific product categories, linking to relevant subcategories and products.
- Use clear anchor text: Ensure clear internal link anchor text in internal links is descriptive. This offers clarity about the linked content.
- Maintain consistency: Keep the structure consistent throughout the site, making it intuitive for users to navigate different sections.
Website hierarchy is your site structure: the organization and placement of content and internal pages on your website. It influences user experience, search engine visibility, and the overall organizational structure of your e-commerce business. By implementing these tips, you create a website easy for your audience to operate and buy from.

Distributing Authority and Relevance
Authority refers to a web page’s perceived importance or credibility, often measured by the quantity and quality of incoming internal links. Relevance is how well a webpage aligns with a user’s search intent.
For e-commerce websites, possessing high authority and relevance is essential.
Here are some tips:
- Prioritize high-value pages: Internally link from high-authority pages to boost the ranking power of important target pages.
- Create hub pages: Establish hub pages that consolidate information on specific topics as authoritative sources linked to relevant content.
- Strategic product interlinking: Link related product categories and subcategories to share ranking power and reinforce thematic relevance.
A site with authority is more likely to rank higher in search engine results. Meanwhile, relevance ensures that your content meets the specific needs of your users, driving organic traffic. A robust internal link structure will ensure that well-ranking pages on your site share it with other pages.
Anchor Text Optimization: Using Descriptive Text for Internal Links
Anchor text refers to the clickable text within a hyperlink. It’s a concise descriptor that provides users and search engines with a preview of the linked content.
When running an e-commerce website, descriptive anchor text is key. It enhances user understanding of linked content and contributes to on-page SEO by providing context and relevance signals for crawlers.
The key word is specificity: Use specific product names or attributes to convey what users can expect from the internal link. Implement exact match anchor text whenever possible. Also, include relevant keywords as anchors when internal linking for SEO. Lastly, use language that prompts users to click and explore whenever possible.

Contextual Relevance: Linking Related Content for Enhanced User Understanding
Contextual relevance in internal linking provides customers with a seamless and logical flow between related content. Contextual links are necessary for businesses that have a wide range of products. It helps users discover products, accessories, or additional information related to their initial search.
Here are some tips for linking related content:
- Create product bundles: Link individual product pages to curated bundles or sets.
- Link accessories: Connect product pages with relevant accessories or compatible items.
- Utilize buying guides: Link products to comprehensive buying guides for in-depth understanding.
- Implement category linking: Connect product pages within the same category for a cohesive shopping experience.
- Ensure strategic upselling and cross-selling: Link-related products to encourage users to explore complementary options.
When users encounter links to relevant pages, it enhances their understanding of your product’s overall product range, specifications, and related information. This creates a more intuitive and enjoyable browsing experience, reducing the friction of them availing of your service.
Deep Linking: Linking to Specific Pages within Your Site’s Architecture
Deep linking is when you create hyperlinks directly to specific pages deep in your website’s architecture, bypassing the homepage or main navigation. There are several ways to implement deep linking for your website.
Let’s see them below:
- Product Page Linking: Deep link directly to product pages from promotional banners or related content.
- Category Deep Links: Connect users to specific categories from relevant sections of your site.
- Featured Item Links: Deep link from featured items on the homepage to drive attention to specific products.
- Newsletter Deep Links: Include deep links in newsletters to direct subscribers to targeted promotions or products.
- Blog Post Integration: Link blog posts to specific product or category pages for seamless integration.
This practice lets potential customers directly access product pages, category pages, or relevant content without going through your website’s upper levels. Users quickly get what they’re looking for by avoiding generic links.
From an SEO perspective, deep linking distributes ranking power efficiently across various pages, contributing to improved search engine visibility.
Linking to Pillar Pages and Cornerstone Content
Pillar pages and cornerstone content are similar – they are both critical pages for your e-commerce website. Pillar pages are comprehensive, broadly themed content pages detailing a specific topic. Cornerstone content is a website’s most valuable and essential piece, often interlinked with related content, forming the foundation of your site architecture.
Here are ways to maximize pillar pages and cornerstone content for your online business:
- Interlink specific pages to broader categories: Link related product pages to relevant pillar content for a holistic customer journey. Also, link to hub pages linking to both pillar content and related products or categories.
- Implement breadcrumb navigation: Use breadcrumbs linking back to cornerstone content to provide context.
- Place prominent links on your home page: Feature links to cornerstone content on the homepage for increased visibility.
Linking to these important pages is critical for your e-commerce website. It reinforces the overall site structure and consolidates authority on specific traffic for your search rankings. This practice also makes it easier for your audience to explore your site based on their needs, further developing trust and credibility.

Fixing Broken Internal Links: Maintaining a Smooth User Experience and SEO Value
Broken internal links are hyperlinks within a website that lead to non-existent or inaccessible pages. They occur due to changes in site structure, deleted content, or URL modifications.
This is critical, especially when your audience clicks on a link that leads them nowhere, they’ll probably exit your website in annoyance. Most internal links on your website should be functioning.
To ensure this, conduct regular audits, implement 301 redirect or 302 redirect for pages that have been moved or deleted, leverage online tools (like Ahrefs Site Explorer and Google Search Console), and keep the XML sitemap current.
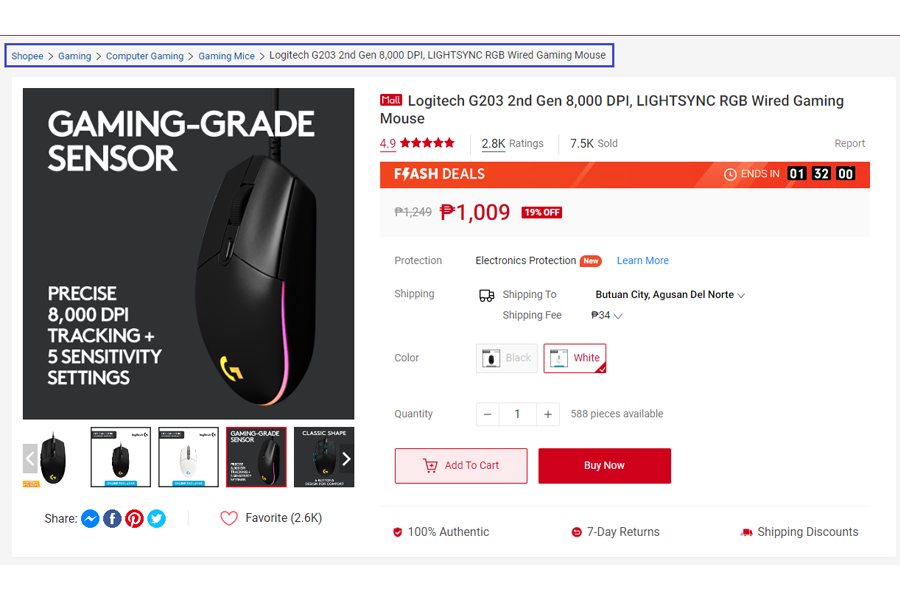
Breadcrumb Navigation: Enhancing User Navigation and Website Crawlability
Breadcrumb navigation is a hierarchical navigation system, often displayed on your webpage, that your customers can use to trace their path back to the homepage. As you can see in the example above, breadcrumb navigation is highly convenient for your audience to navigate. It gives them a clear, concise trail that lets them know where they are.
Breadcrumb navigation also enhances website crawlability, aiding search engines in understanding the site’s structure and the relationships between different pages.
When implementing, ensure each breadcrumb link is clear and descriptive, use schema markup, and always check that breadcrumbs lead to related and logical pages.
Linking to High-Value and Evergreen Content
You know your content is high-value when it provides information-rich, engaging, and high-ranking materials to your audience. On the other hand, you know it’s evergreen when it stays relevant over a long time.
These types of content serve as anchors for e-commerce websites like yours. They attract and retain visitors, showcase expertise, and contribute to sustained SEO benefits. High-value content engages users, while evergreen content ensures a lasting impact, driving continuous traffic.
Integrate internal links from prominent pages to high-value and evergreen content. You should also regularly update content and create internal links between related high-value and evergreen content.
Internal Links and Topic Clusters: Strengthening Content Connections for SEO
Topic clusters are a content organization strategy where a pillar page covering a broad topic is linked to and from cluster content pages that delve into specific aspects or subtopics related to the main theme.
Internal linking with topic clusters is an excellent SEO strategy because it signals your comprehensive coverage of a particular subject to search engines.
Ensure anchor text indicates the content’s context for users and search engines, develop hub pages that act as central points, and feature links related to the cluster content on high-traffic pages.
These techniques boost the pillar page’s authority and improve the overall ranking of connected cluster content, ultimately driving more eyeballs to your content and more traffic to your site.
External Linking Considerations: Balancing Internal and External Link Strategies
While internal linking connects your page to other site pages, external links connect you to pages from other websites. Both strategies are crucial in any good SEO strategy.
Below, we will see some best practices to ensure that you balance internal and external efforts when planning your content promotion and link building strategy.
Let’s see them in detail:
- Prioritize user experience: Internal links should guide users through your content, while external links must provide additional valuable information.
- Ensure strategic authority distribution: Use internal links for distributing authority within your website. Use reputable external links to boost overall credibility.
- Keep relevance top-of-mind: Ensure both internal and external links are contextually relevant to where it’s contained. This enhances user understanding and search engine recognition.
- Maintain a natural flow: Avoid overloading with links. Too many links can be a nuisance to both audience and search engines alike. Let the content dictate the need for both internal and external references.
- Regularly audit your links: Periodically review and update both internal and external links to adapt to changes in content and the online landscape.
Internal linking enhances user experience, guides navigation, and distributes authority across your website. It also establishes a structural hierarchy that aids search engines in understanding your site’s architecture and content relationships.
External linking contributes to your site’s authority and credibility. When your site demonstrates connections to reputable external sources, search engines view this as a signal of content reliability and relevance.

Final Thoughts
E-commerce websites are becoming everyone’s solution to stand out in the crowded online space, but not everyone is doing it right. This is your opportunity.
An excellent internal link-building strategy is what you need to stand out from the rest of your competitors online. Without robust internal links balanced with a sound external link strategy, your content will get buried under the pile of thousands of businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many internal links do you need?
We know internal links are important, but how many links does your website need? The ideal number varies based on your website’s content and structure. Focus on creating internal links that enhance user experience and provide value.
Does internal linking affect SEO?
Internal linking is critical for SEO, as it significantly impacts SEO performance. It helps search engines understand your site’s structure, establishes content hierarchy, and distributes authority, so multiple internal links on your web page boost SEO.
What are nofollow links and dofollow links?
Nofollow links instruct search engines not to pass authority to the linked page, often used for paid links or user-generated content, indicating that the linked page shouldn’t be endorsed. On the other hand, dofollow internal links allow the transfer of authority. They are standard links contributing to SEO and page authority.